
Tundish nozzle is one of the key components in continuous steel casting process. These nozzles are used to control and direct the flow of molten steel from the furnace to the casting molds. Tundish nozzle plays a vital role in guaranteeing the quality and uniformity of final steel products. These nozzles provide the possibility of producing steel products with desirable dimensions and characteristics by accurately controlling the melt flow. Among the features that Tundish nozzles should have are high thermal resistance, resistance Against corrosion and wear and precise design.The constituent components of the Tundish nozzle are the nozzle body, the nozzle edge, the cooling system, etc. The casting nozzle, by combining outstanding technical features and quality components, plays a very important role in improving the steel casting process and producing high quality products. This article is fully discussed in the context of the definition of Tundish nozzle, the role and weaknesses of the nozzle, the types and components of Tundish nozzle. Stay with us until the end.
A Tundish Nozzle is one of the crucial components in the continuous casting process in the steelmaking industry. The tundish acts as an intermediary chamber between the ladle containing molten steel and the casting mold, playing an essential role in evenly distributing the molten steel and controlling its flow into the molds. As the name suggests, the tundish nozzle is located at the bottom of the tundish and helps regulate and control the flow of molten steel into the mold.

: Control of Molten Steel Flow
The tundish nozzle controls the flow rate of molten steel by adjusting the outlet diameter, ensuring the molten steel flows uniformly and controllably into the mold.
: Prevention of Contamination
The tundish nozzle helps reduce the entry of impurities and contaminants into the molten steel flow.
: Reduction of Turbulence
Using a tundish nozzle makes the molten steel flow smoother and less turbulent into the mold, improving the final product's quality.
: Increasing Equipment Lifespan
By controlling temperature and flow, the tundish nozzle prevents rapid wear and corrosion of equipment, thereby extending their useful life.
Ceramic Nozzles :These nozzles are made from heat-resistant materials and are suitable for high temperatures.
Metal Nozzles :Typically made from steel or heat-resistant alloys.
Composite Nozzles :A combination of ceramic and metal materials, offering the advantages of both types.
Single Bore Nozzles :Feature a single passage for molten steel flow.
Multi Bore Nozzles :Have multiple passages for molten steel flow.
Flow Control Nozzles :Equipped with mechanisms to precisely regulate and control the flow of molten steel.
Read more: Supplier of machinery, equipment, materials and industrial parts from Iran with Shamsta
Various materials are used in the construction of tundish nozzles, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most important characteristics of the materials used include heat resistance, corrosion and wear resistance, and chemical stability. Some of the materials used are as follows:
**Alumina (Al₂O₃): Due to its high resistance to temperature and wear, alumina is one of the primary materials used in the construction of tundish nozzles.
**Zirconia (ZrO₂): With very high thermal resistance and resistance to thermal shocks, zirconia is also widely used.
**Silicon Carbide (SiC): Due to its corrosion and wear resistance, silicon carbide is applied in the construction of tundish nozzles.
**Mullite (3Al₂O₃·2SiO₂): Known for its strength and resistance to thermal shock, mullite is used in the composition of tundish nozzle materials.
**Graphite: As a heat-resistant material with lubricating properties, graphite is used in some tundish nozzles.
**Carbon: For improved resistance to wear and thermal shock, carbon is used in some tundish nozzle compositions.
**Composite Refractory Materials: These materials combine several refractory materials such as alumina and zirconia to enhance the mechanical and thermal properties of the nozzles.
With the proper combination and precise design, these materials can optimize tundish nozzles to withstand the harsh conditions of steel casting.
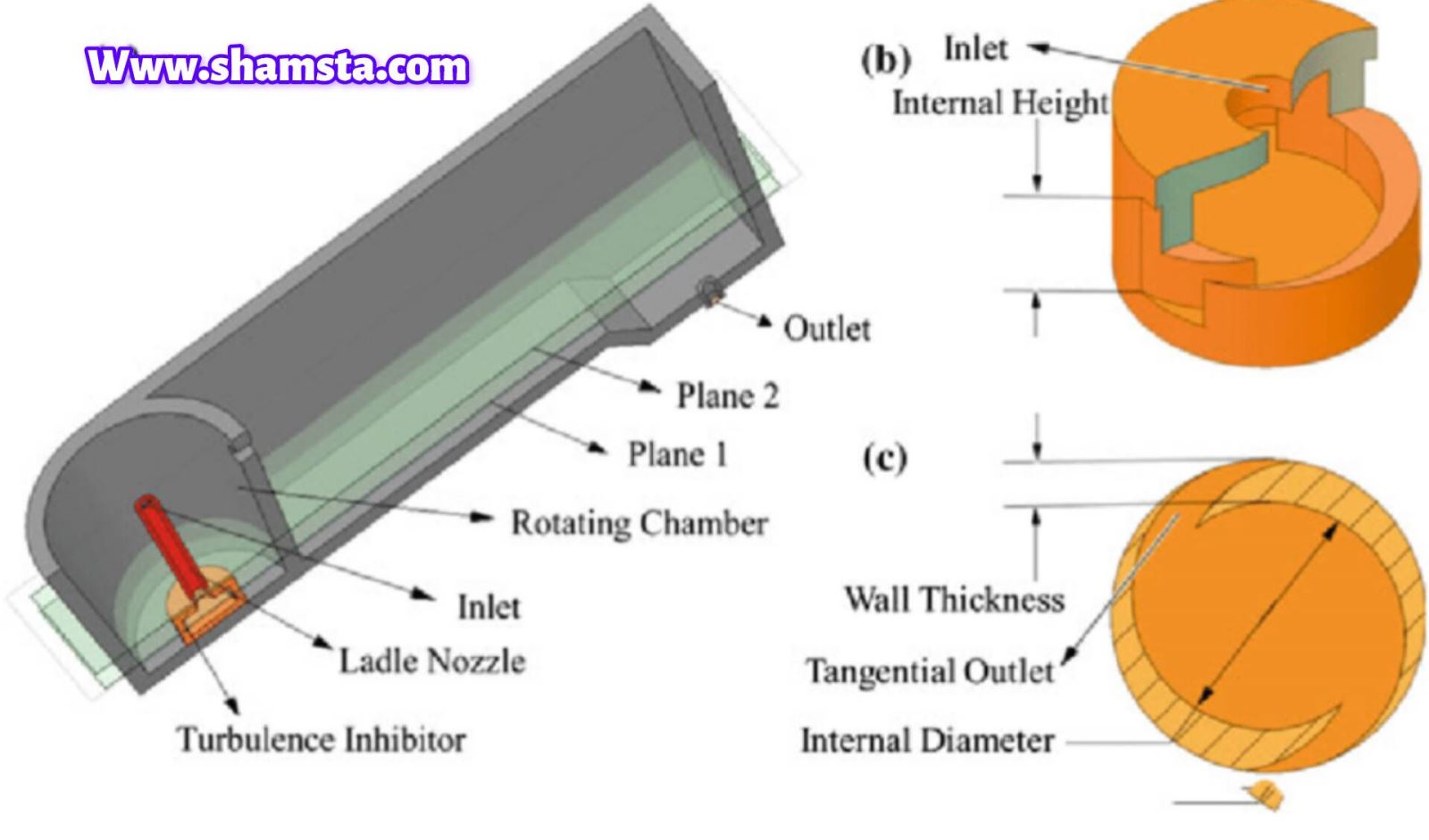
The components of a tundish nozzle generally include various parts, each playing a specific role in the nozzle's performance. These components are as follows:
**Nozzle Body: The nozzle body is made of materials with high thermal and mechanical resistance and forms the main structure of the nozzle. It must withstand high temperatures and the pressure of molten metal.
Nozzle Tip: The sensitive part of the nozzle that comes into direct contact with molten steel. It is made from materials highly resistant to heat and wear.
Internal Lining: A layer used to increase the nozzle's resistance to corrosion and wear, typically made from refractory materials such as alumina or zirconia.
Cooling System: Some nozzles have a cooling system designed to control the nozzle's temperature and extend its useful life. This system can include water or air cooling channels.
Seals and Gaskets: Components used to prevent the leakage of molten steel and maintain the nozzle's efficiency. These must be resistant to high heat and pressure.
Nozzle Cap or Cover: The top part of the nozzle, used to protect and shield the nozzle from external damage. It is usually made from durable and lightweight materials.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection:
To prevent failure and ensure product quality, tundish nozzles must be regularly inspected and maintained.
Precise Adjustment:
Accurate adjustment of the diameter and position of the tundish nozzle is crucial to controlling the molten steel flow optimally.
Use of High-Quality Materials:
Using high-quality materials in the construction of tundish nozzles helps increase their lifespan and performance.
Wear and Corrosion :Due to the high temperature of molten steel, tundish nozzles are prone to rapid wear and corrosion.
Blockage :The entry of impurities and contaminants can cause nozzle blockage.
Temperature Variations :Sudden temperature changes can lead to cracking and damage to the nozzle.
Overall, the tundish nozzle is a key component in the continuous casting process, playing a crucial role in controlling and improving the quality of produced steel. Given the harsh working conditions, using durable materials and regular maintenance is of utmost importance.
.jpg)
Tundish nozzles are primarily used in the steelmaking industry and in the continuous casting process. Their main applications are as follows:
Steelmaking Industry
Continuous Casting:
- Tundish: The tundish nozzle is installed at the bottom of the tundish and directs the molten steel in a controlled and uniform manner into the casting molds. This helps prevent turbulence and contamination in the molten stream, improving the final product's quality.
- Flow Control: By regulating the molten steel flow, the tundish nozzle helps maintain the appropriate temperature and reduce mold wear.
Precision Casting:In precision casting processes requiring high accuracy and surface quality, the tundish nozzle helps control the molten metal flow more precisely and distribute it evenly.
Automotive Industry: In the production of automotive parts requiring high-quality steel, using a tundish nozzle aids in producing steel with better mechanical properties and reducing surface defects.
Construction Industry:In the production of construction steel, such as beams, rebars, and steel sheets, the use of tundish nozzles helps improve mechanical properties and reduce surface defects.
Oil and Gas Industry:In the production of pipes and equipment used in the oil and gas industry, where high resistance to corrosion and pressure is required, using a tundish nozzle helps improve steel quality and resistance.
Machinery Manufacturing:In the production of heavy machinery and industrial equipment, tundish nozzles help produce steel with suitable mechanical properties and reduce defects in parts.
Shipbuilding Industry:In the construction of ship hulls and equipment requiring durable and robust steel, tundish nozzles help improve the quality of the produced steel.
- Precise Flow Control: Prevents turbulence and contamination in the molten steel flow.
- Quality Improvement: Reduces surface defects and enhances the mechanical properties of the final product.
- Increased Equipment Lifespan: Reduces wear and corrosion of molds and casting equipment.
- Cost Reduction: Enhances productivity and reduces the need for frequent repairs.